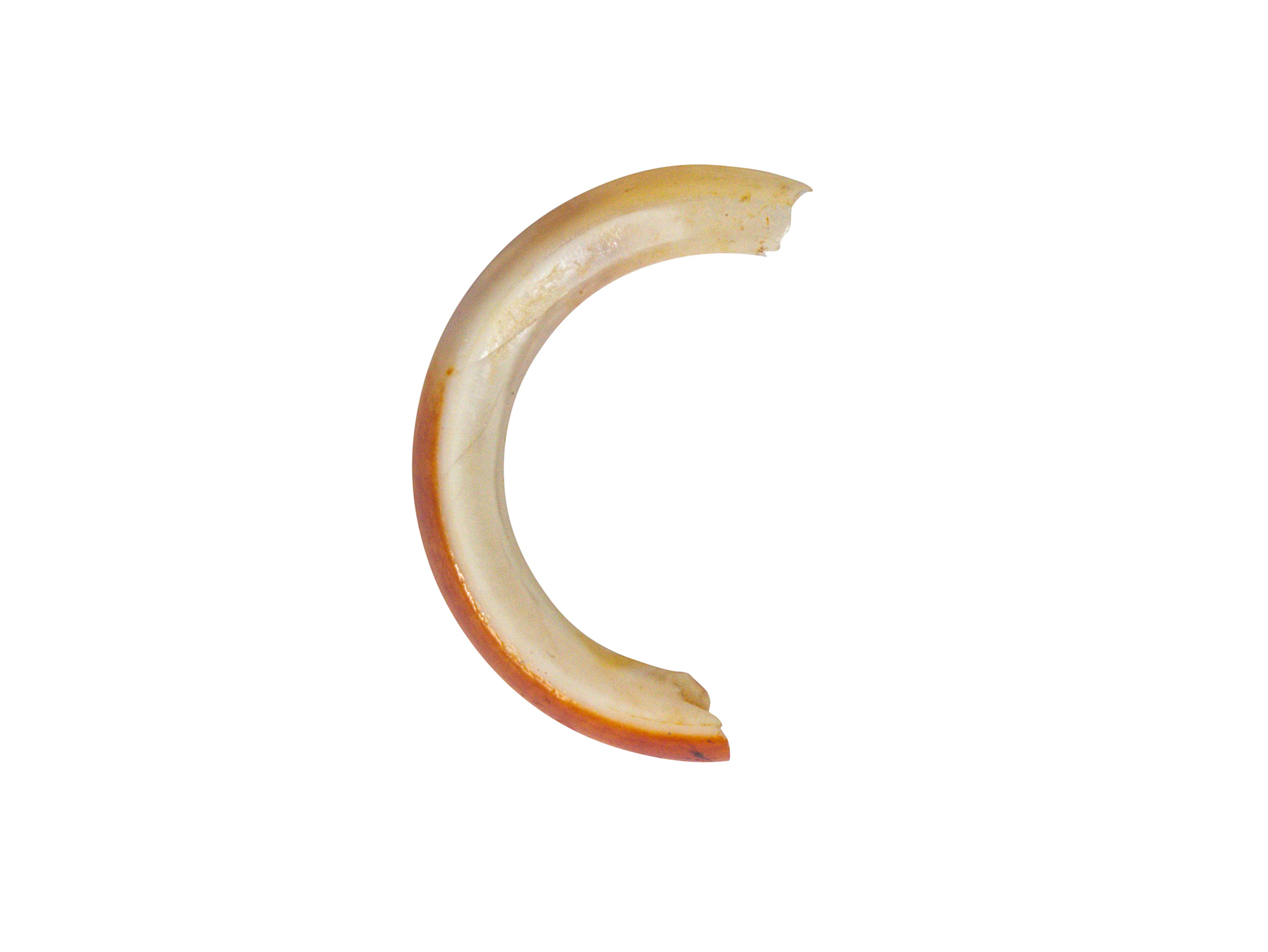
Beaver teeth are a fascinating example of evolutionary adaptation. These remarkable rodents are known for their impressive dental structure, which allows them to efficiently fell trees, build dams, and create intricate habitats. Understanding the unique characteristics of beaver teeth can provide valuable insights into both natural engineering and dental science. As one of nature's most efficient chewing machines, beaver teeth demonstrate how specialized dental structures can impact an entire ecosystem.
These remarkable creatures possess teeth that are perfectly adapted to their lifestyle and habitat. The distinctive orange enamel, self-sharpening ability, and continuous growth of beaver teeth have intrigued scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. This article will explore the intricate details of beaver dental structure, their maintenance mechanisms, and the crucial role these teeth play in ecosystem development.
As we delve deeper into the world of beaver teeth, we'll uncover how these dental adaptations have influenced human engineering and inspired modern dental solutions. From their unique composition to their practical applications in nature, beaver teeth represent a perfect example of evolutionary success that continues to impact various fields of study.
Read also:Unveiling The Mysteries Of The 1967 Chinese Zodiac Animal The Year Of The Fire Goat
Table of Contents
Anatomy of Beaver Teeth
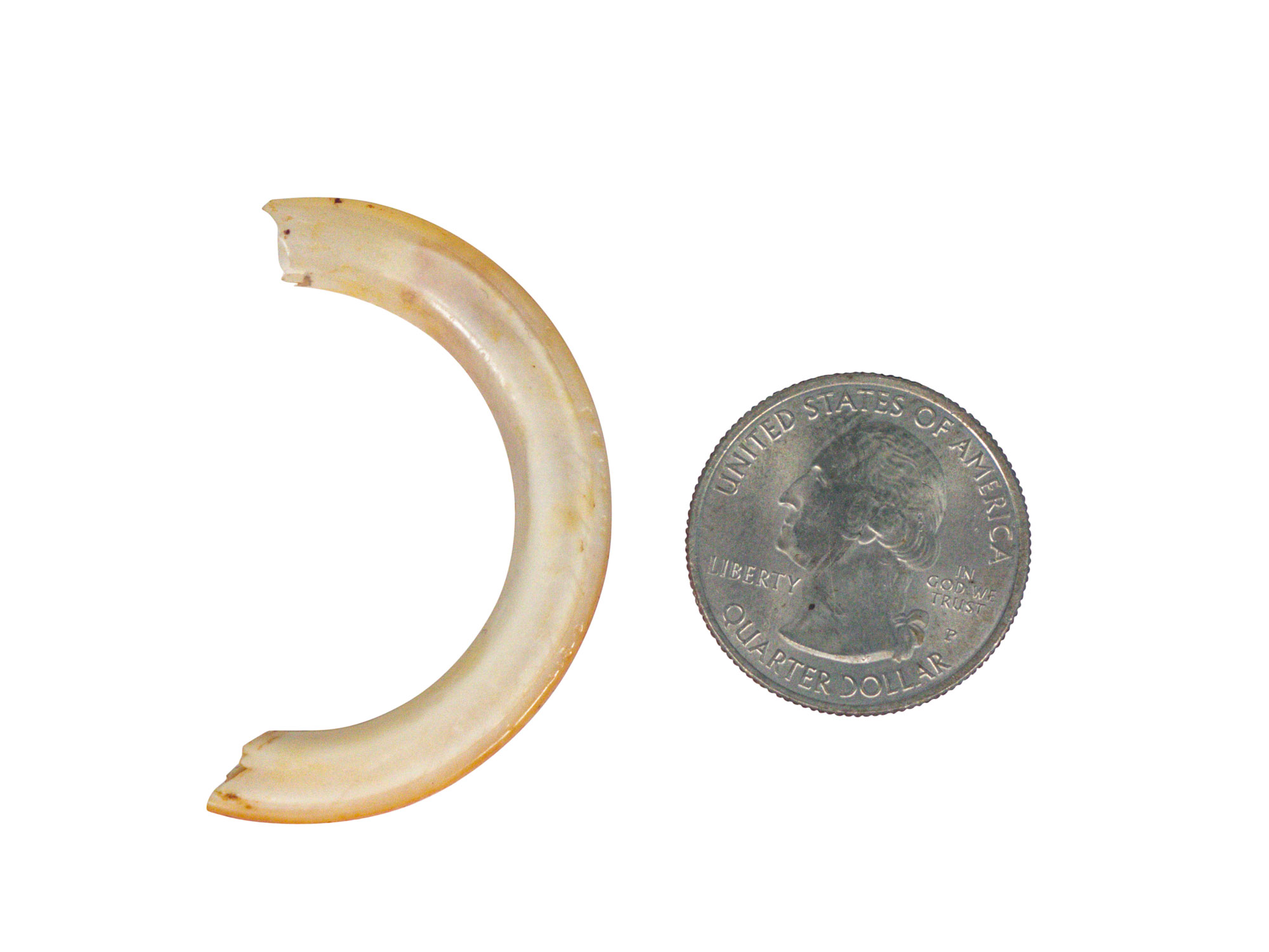
Beaver teeth possess a distinctive anatomy that sets them apart from other mammals. The most noticeable feature is their prominent incisors, which are perfectly adapted for their wood-cutting lifestyle. These incisors measure approximately 20-25mm in length and feature a unique orange enamel coating on the front surface. This distinctive coloration results from iron-rich pigmentation, which provides exceptional strength and resistance to wear.
Key Characteristics
- Four prominent incisors - two upper and two lower
- Distinct orange enamel on the front surface
- Softer dentin on the back surface
- Curved shape for efficient wood cutting
- Continuous growth throughout their lifespan
The structural design of beaver teeth creates a natural self-sharpening mechanism. As they chew, the softer dentin on the back wears away faster than the iron-reinforced enamel on the front. This differential wear pattern maintains a sharp cutting edge, allowing beavers to efficiently process wood throughout their lives.
Continuous Growth Mechanism
One of the most remarkable aspects of beaver teeth is their continuous growth pattern. These incisors grow at an impressive rate of approximately 4mm per week, a necessary adaptation to counteract the extensive wear from their constant chewing activities. This growth pattern is crucial for maintaining the beaver's ability to process food and construct their habitats.
Growth Regulation Factors
- Genetic programming for consistent growth
- Hormonal regulation of dental development
- Nutritional factors influencing growth rate
- Environmental impact on dental health
This continuous growth mechanism serves as a natural insurance policy against dental wear. However, it also requires careful management through regular use. If a beaver's teeth aren't worn down properly through natural chewing activities, they can become overgrown, leading to potential health issues and affecting the animal's ability to feed and build.
Unique Composition and Structure
The composition of beaver teeth represents a remarkable example of biological engineering. The outer enamel layer contains high concentrations of iron, which gives it the characteristic orange color and exceptional durability. This iron-rich enamel is approximately three times harder than human tooth enamel, providing beavers with the necessary strength to cut through wood efficiently.
Microscopic analysis reveals a sophisticated structure beneath the surface. The enamel consists of tightly packed hydroxyapatite crystals reinforced with iron oxide, creating a material that resists wear and cracking. The inner dentin layer, while softer, serves an equally important purpose in the tooth's function. This differential hardness between enamel and dentin creates the self-sharpening mechanism that maintains the teeth's cutting efficiency.
Read also:Jim Carreys Girlfriend In 2025 A Deep Dive Into His Love Life
Recent studies have shown that the chemical composition of beaver teeth enamel includes approximately 18% iron by weight, compared to less than 1% in human teeth. This high iron content contributes to its remarkable resistance to acid erosion and mechanical wear, making it one of nature's most durable biological materials.
Functional Adaptations
Beaver teeth serve multiple critical functions in their daily lives, each adapted to their specific ecological niche. The primary function revolves around their ability to efficiently process wood, which serves both nutritional and construction purposes. Their incisors can exert tremendous pressure, estimated at over 170 pounds per square inch, allowing them to fell trees up to 40 inches in diameter.
Primary Functions
- Tree felling for dam construction
- Food processing and bark stripping
- Habitat modification and creation
- Defense mechanism against predators
The shape and angle of beaver incisors enable precise cutting techniques that minimize energy expenditure. Their teeth work in a scissor-like motion, with upper and lower incisors meeting at a precise angle that maximizes cutting efficiency. This adaptation allows beavers to process wood quickly, often felling trees within minutes and creating complex aquatic environments that benefit numerous other species.
Natural Maintenance System
Beavers have evolved an ingenious system for maintaining their teeth, crucial for their survival and ecological role. The natural maintenance process begins with their daily activities, particularly their extensive chewing habits. Each time a beaver chews, the differential wear between the hard enamel and softer dentin automatically sharpens their incisors, maintaining an optimal cutting edge.
Maintenance Mechanisms
- Regular chewing on hard materials
- Self-sharpening through differential wear
- Natural alignment through opposing tooth contact
- Behavioral adaptations to prevent overgrowth
In addition to mechanical maintenance, beavers have developed behavioral patterns that support dental health. They instinctively gnaw on specific types of wood and bark that provide the right balance of resistance and nutrition. This natural selection of chewing materials helps maintain their teeth at the proper length and sharpness while also providing essential nutrients for continued dental development.
Ecological Impact
The impact of beaver teeth extends far beyond the individual animals, creating profound effects on entire ecosystems. Through their tree-cutting activities, beavers engineer aquatic environments that support diverse plant and animal communities. Studies show that areas modified by beaver activity can increase biodiversity by up to 33%, creating habitats for numerous species including fish, amphibians, and waterfowl.
Beaver-created wetlands play a crucial role in water management and filtration. These engineered environments can store up to 10 times more water than natural wetlands, providing essential flood control and groundwater recharge. The trees felled by beavers create natural debris dams that further enhance habitat complexity and water retention capabilities.
Research conducted by the University of Alberta demonstrates that beaver-modified landscapes can sequester up to 50% more carbon than unmodified areas. This environmental benefit, driven by their dental capabilities, highlights the significant role these animals play in climate regulation and ecosystem health.
Evolutionary Significance
The evolutionary history of beaver teeth provides fascinating insights into adaptive radiation and natural selection. Fossil records indicate that the earliest beaver ancestors appeared approximately 24 million years ago, with dental adaptations evolving significantly over time. The development of iron-rich enamel likely emerged as a response to increased demand for wood processing in their changing environments.
Evolutionary Milestones
- Development of iron-reinforced enamel
- Emergence of continuous growth mechanism
- Refinement of self-sharpening system
- Adaptation to diverse environmental conditions
Comparative studies of modern and ancient beaver species reveal gradual improvements in dental efficiency. The current dental structure represents millions of years of refinement, optimized for maximum durability and functionality. This evolutionary journey demonstrates how specific adaptations can drive ecological success and influence entire ecosystems over geological timescales.
Dental Health Insights
Beaver teeth offer valuable lessons for human dental health and biomimetic research. The unique iron-rich enamel composition has inspired new approaches to dental materials science, with researchers exploring similar mineral structures for human dental applications. Studies have shown that the incorporation of iron compounds in dental materials can increase wear resistance by up to 40%.
The self-sharpening mechanism of beaver teeth has influenced the development of new dental instruments and maintenance techniques. Dental researchers have adapted this principle in designing more durable dental implants and restorative materials. The differential hardness concept has led to innovations in composite materials used for dental fillings and crowns.
Recent advances in biomimetic dentistry have focused on replicating the natural maintenance system observed in beavers. This research has led to improved understanding of how mechanical stress and material composition interact to maintain dental health, potentially revolutionizing preventive dental care and treatment approaches.
Human Applications and Inspiration
The study of beaver teeth has significantly influenced various fields of human innovation and engineering. In materials science, researchers have developed new cutting tools inspired by the beaver's iron-rich enamel, resulting in blades that maintain sharpness up to 60% longer than traditional materials. This has led to breakthroughs in industrial cutting equipment and surgical instruments.
Practical Applications
- Development of self-sharpening cutting tools
- Innovations in dental materials technology
- Advancements in construction engineering
- Improved water management systems
Architects and engineers have adopted beaver-inspired designs for sustainable water management systems. These nature-based solutions have been implemented in urban planning projects, demonstrating up to 40% improvement in flood control efficiency. The principles of natural ecosystem engineering observed in beaver behavior have also influenced modern green infrastructure development.
Conservation and Protection
Protecting beaver populations and their dental health is crucial for maintaining ecosystem balance. Conservation efforts focus on preserving natural habitats that support proper dental development and function. The North American Beaver Conservation Initiative reports that protected habitats show a 25% increase in beaver population health, directly correlating with improved dental condition.
Current conservation strategies include habitat restoration projects, protection of key food sources, and monitoring of environmental factors affecting dental health. Researchers have identified specific mineral requirements necessary for maintaining optimal enamel development, leading to targeted conservation approaches that ensure adequate nutritional resources in beaver habitats.
Conclusion
Beaver teeth represent a remarkable example of evolutionary perfection, demonstrating how specialized dental structures can shape ecosystems and inspire human innovation. From their iron-reinforced enamel to their self-sharpening mechanism, these remarkable dental adaptations continue to influence fields ranging from materials science to ecological engineering.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences regarding beaver teeth and their impact on natural systems. Have you observed beaver activity in your local environment? How might the principles of beaver dental adaptation be applied to human technology? Please leave your comments below and join the conversation about these fascinating creatures.
For more information about wildlife conservation and ecological engineering, explore our related articles on sustainable ecosystem management and nature-inspired innovations. Your engagement helps spread awareness about the importance of preserving these remarkable animals and their unique adaptations.