Elephants are among the most fascinating and iconic animals on the planet. These gentle giants have captured the hearts of people worldwide with their intelligence, social behavior, and sheer size. Whether you’re an animal enthusiast, a wildlife conservationist, or simply curious about these magnificent creatures, this article will provide you with an in-depth understanding of elephants. From their unique characteristics to their role in ecosystems and the challenges they face, we’ll explore everything you need to know about elephants.
Elephants have been an integral part of human culture and history for centuries. They are revered in many societies and are often seen as symbols of wisdom, strength, and loyalty. However, despite their cultural significance, elephants face numerous threats today, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Understanding these challenges is crucial to ensuring the survival of these incredible animals for future generations.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of elephants, covering their biology, behavior, conservation status, and much more. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of why elephants are so important and what we can do to protect them. Let’s embark on this journey to discover the wonders of the elephant list.
Read also:Kevin Leonardo Nair The Rising Star In The Digital World
Table of Contents
- Elephant Biology: Anatomy and Physical Characteristics
- The Three Main Species of Elephants
- Elephant Behavior and Social Structure
- Elephant Habitats and Ecosystem Roles
- Conservation Status and Threats to Elephants
- Elephants in Culture and Human History
- Global Conservation Efforts for Elephants
- Interesting Facts About Elephants
- Ongoing Research and Discoveries About Elephants
- The Future of Elephants: Challenges and Opportunities
Elephant Biology: Anatomy and Physical Characteristics
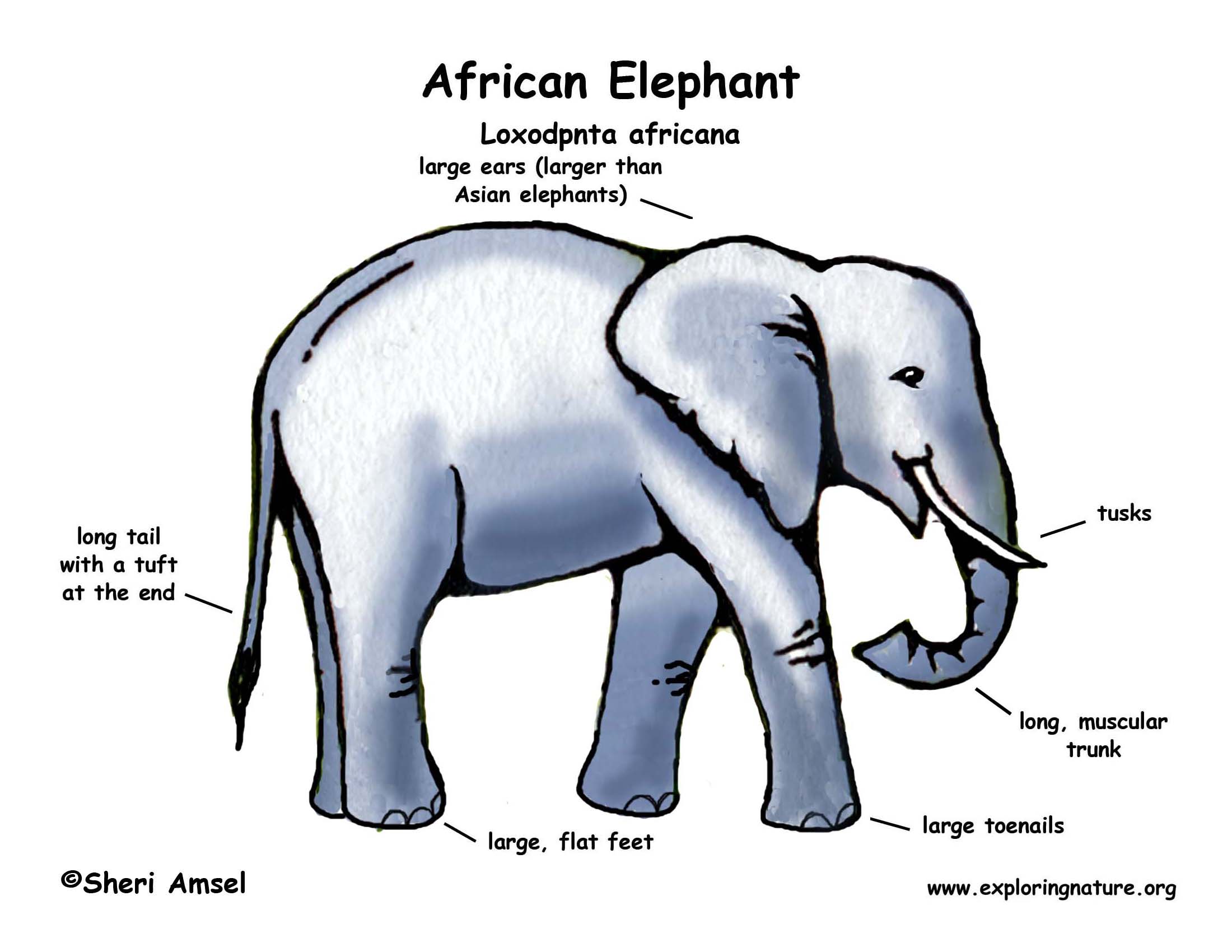
Elephants are the largest land animals on Earth, and their physical characteristics are nothing short of remarkable. Their most distinctive feature is their trunk, a versatile organ used for breathing, smelling, touching, grasping, and producing sounds. The trunk contains over 40,000 muscles, making it incredibly strong and flexible.
Another defining characteristic of elephants is their tusks. These elongated incisor teeth are used for digging, stripping bark from trees, and as weapons in defense or combat. Unfortunately, tusks have also made elephants a target for poachers seeking ivory.
Elephants also have large, fan-like ears that help regulate their body temperature. By flapping their ears, they can cool down their blood and maintain a stable internal temperature. Their thick, wrinkled skin helps retain moisture and provides protection from the sun and insect bites.
The Three Main Species of Elephants
African Savanna Elephant
The African savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana) is the largest elephant species and is primarily found in grasslands and open woodlands across sub-Saharan Africa. These elephants can weigh up to 6 tons and stand up to 13 feet tall at the shoulder. They are known for their large ears, which resemble the shape of the African continent.
African Forest Elephant
The African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis) is smaller and darker than its savanna counterpart. It inhabits the dense rainforests of West and Central Africa. This species plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of forest ecosystems by dispersing seeds and creating clearings for new plant growth.
Asian Elephant
The Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) is native to Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. It is smaller than African elephants, with a more rounded back and smaller ears. Asian elephants are often used in cultural and religious ceremonies, particularly in countries like Thailand and India.
Read also:Julia Roberts Today Age A Comprehensive Look At Her Life Career And Influence
Elephant Behavior and Social Structure
Elephants are highly social animals that live in matriarchal herds. These herds are typically led by the oldest and most experienced female, known as the matriarch. The matriarch guides the group to food and water sources and ensures the safety of the herd.
Elephants communicate using a variety of vocalizations, body language, and even seismic signals. Their low-frequency rumbles can travel over long distances, allowing them to stay in touch with herd members who may be far away.
One of the most remarkable aspects of elephant behavior is their ability to grieve. Elephants have been observed mourning their dead, often staying near the body of a deceased herd member for extended periods. This behavior highlights their deep emotional connections and intelligence.
Elephant Habitats and Ecosystem Roles
Elephants are keystone species, meaning they play a critical role in shaping their ecosystems. By uprooting trees and trampling vegetation, they create open spaces that benefit other species. Their dung also serves as a fertilizer, spreading seeds and nutrients across the landscape.
African elephants are typically found in savannas, grasslands, and forests, while Asian elephants inhabit tropical forests, grasslands, and scrublands. Unfortunately, habitat loss due to human activities such as agriculture and urbanization is a major threat to elephant populations worldwide.
Conservation Status and Threats to Elephants
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), both African and Asian elephants are classified as endangered or vulnerable. The primary threats to their survival include poaching for ivory, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict.
Poaching has decimated elephant populations in many parts of Africa and Asia. Despite international bans on ivory trade, illegal poaching remains a significant problem. Conservation organizations and governments are working tirelessly to combat this issue through anti-poaching patrols and stricter enforcement of wildlife laws.
Elephants in Culture and Human History
Elephants have been revered in many cultures throughout history. In Hinduism, the elephant-headed god Ganesha is worshipped as the remover of obstacles. In Buddhism, elephants symbolize mental strength and wisdom.
Historically, elephants have been used in warfare, transportation, and labor. Their strength and intelligence made them invaluable assets in ancient civilizations. Today, elephants continue to hold a special place in human culture, often featured in art, literature, and folklore.
Global Conservation Efforts for Elephants
Conservation efforts for elephants are underway across the globe. Organizations such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) are actively working to protect elephant habitats, reduce poaching, and promote coexistence between humans and elephants.
Community-based conservation programs have also proven effective in reducing human-wildlife conflict. By involving local communities in conservation efforts, these programs help create sustainable livelihoods while protecting elephant populations.
Interesting Facts About Elephants
- Elephants can recognize themselves in mirrors, a sign of self-awareness found in only a few species.
- They can live up to 70 years in the wild.
- Elephants are excellent swimmers and can use their trunks as snorkels when crossing deep water.
Ongoing Research and Discoveries About Elephants
Scientists continue to study elephants to better understand their behavior, communication, and cognitive abilities. Recent research has revealed that elephants can distinguish between human languages and even recognize individual human voices.
Advances in technology, such as GPS tracking and camera traps, are providing valuable insights into elephant movements and habitat use. These tools are helping conservationists develop more effective strategies for protecting elephant populations.
The Future of Elephants: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of elephants depends on our ability to address the challenges they face. By supporting conservation initiatives, reducing demand for ivory, and promoting sustainable development, we can help ensure that these majestic creatures continue to thrive.
Individuals can contribute by raising awareness, supporting wildlife organizations, and making environmentally conscious choices. Together, we can create a brighter future for elephants and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, elephants are remarkable creatures that play a vital role in our ecosystems and cultures. From their unique biology and social behavior to their conservation challenges, the elephant list is a testament to their importance in the natural world. By understanding and addressing the threats they face, we can help secure a future where elephants continue to roam freely.
We encourage you to share this article with others, leave a comment with your thoughts, or explore more content on our website. Together, we can make a difference for these incredible animals.