When it comes to cooking or baking, the terms "heavy whipping cream" and "heavy cream" often cause confusion. Are they the same? Can they be used interchangeably? These are questions that many home cooks and professional chefs alike have asked. Understanding the differences between these two dairy products is essential, especially if you're aiming for precision in your recipes. Both heavy whipping cream and heavy cream play vital roles in creating rich, creamy textures in dishes, from desserts to savory sauces. However, their subtle differences can impact the outcome of your culinary creations. Let's dive deeper into this topic to uncover the truth behind these two commonly used ingredients.
Heavy cream and heavy whipping cream are staples in many kitchens, but their similarities and differences are often misunderstood. While they may seem interchangeable at first glance, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Knowing these nuances will not only improve your cooking but also ensure you achieve the desired results every time. Whether you're whipping up a batch of homemade whipped cream or enriching a soup, understanding these differences is key.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about heavy whipping cream and heavy cream. From their definitions and fat content to their culinary uses and storage tips, we’ll leave no stone unturned. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of when to use each type of cream and how to make the most of them in your recipes. Let’s begin by breaking down the basics of these two ingredients.
Read also:David Gahan The Voice Behind Depeche Modes Success
Table of Contents
- What is Heavy Cream?
- What is Heavy Whipping Cream?
- Key Differences Between Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
- Culinary Uses of Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
- Understanding Fat Content in Cream
- Substitutes for Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
- Storage Tips for Cream Products
- Nutritional Information
- Common Misconceptions About Cream
- Conclusion
What is Heavy Cream?
Heavy cream, also known as heavy whipping cream in some regions, is a rich dairy product with a high fat content. It is typically made by skimming the fat from milk and is characterized by its thick, creamy texture. Heavy cream contains at least 36% milk fat, making it ideal for whipping and creating stable foams. This cream is often used in recipes that require a rich, velvety texture, such as sauces, soups, and desserts.
One of the defining features of heavy cream is its ability to hold its shape when whipped. This makes it a popular choice for creating whipped cream, mousses, and other desserts that rely on aeration. Additionally, heavy cream is often used to add richness to savory dishes, such as creamy pasta sauces or hearty soups. Its high fat content not only enhances flavor but also contributes to a luscious mouthfeel.
Characteristics of Heavy Cream
- Contains at least 36% milk fat.
- Thick and creamy texture.
- Ideal for whipping and creating stable foams.
- Used in both sweet and savory recipes.
Heavy cream is a versatile ingredient that can elevate a wide range of dishes. Whether you're baking a decadent dessert or preparing a comforting meal, heavy cream is a reliable choice for adding richness and depth to your recipes.
What is Heavy Whipping Cream?
Heavy whipping cream is another type of cream that is often used in cooking and baking. Like heavy cream, it has a high fat content, typically around 30-36%. The term "whipping cream" in its name refers to its ability to whip into stiff peaks, making it a favorite for creating whipped cream and other aerated desserts. While heavy whipping cream and heavy cream are similar, there are subtle differences that set them apart.
Heavy whipping cream is slightly lighter than heavy cream in terms of fat content, which can affect its performance in certain recipes. However, it is still an excellent choice for whipping and adding richness to dishes. It is commonly used in recipes that require a lighter texture, such as mousses, puddings, and frostings. Its versatility makes it a staple in many kitchens.
Characteristics of Heavy Whipping Cream
- Contains 30-36% milk fat.
- Whips into stiff peaks for desserts.
- Slightly lighter than heavy cream.
- Used in both sweet and savory dishes.
Heavy whipping cream is a great option for recipes that require a balance of richness and lightness. Its ability to whip into a fluffy texture makes it a popular choice for desserts, while its creamy consistency adds depth to savory dishes.
Read also:Understanding Blaykes Current Age A Comprehensive Guide
Key Differences Between Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
While heavy cream and heavy whipping cream share many similarities, there are key differences that set them apart. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right cream for your recipes and achieve the desired results.
Fat Content
The primary difference between heavy cream and heavy whipping cream lies in their fat content. Heavy cream typically contains at least 36% milk fat, while heavy whipping cream has a fat content of 30-36%. This variation in fat content can affect the cream's ability to whip and hold its shape. Heavy cream is generally better suited for recipes that require a richer, more stable texture, while heavy whipping cream is ideal for lighter, fluffier creations.
Texture and Consistency
Heavy cream has a thicker, richer texture compared to heavy whipping cream. This makes it a better choice for recipes that require a dense, creamy consistency, such as custards and ice creams. On the other hand, heavy whipping cream has a lighter texture, making it perfect for whipped toppings and airy desserts.
Culinary Uses
Both heavy cream and heavy whipping cream are versatile ingredients, but their differences make them better suited for specific applications. Heavy cream is often used in savory dishes, such as creamy soups and sauces, while heavy whipping cream is a favorite for desserts and whipped toppings. Understanding these distinctions will help you make informed decisions when selecting cream for your recipes.
Culinary Uses of Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
Heavy cream and heavy whipping cream are indispensable in the kitchen, offering a wide range of culinary applications. Their rich flavor and creamy texture make them ideal for both sweet and savory dishes. Let's explore some of the most common uses for each type of cream.
Heavy Cream in Savory Dishes
Heavy cream is a staple in many savory recipes, thanks to its high fat content and ability to add richness. It is often used to create creamy sauces, such as Alfredo or béchamel, and is a key ingredient in soups like clam chowder and cream of mushroom. Heavy cream can also be used to enrich risottos, mashed potatoes, and casseroles, providing a velvety texture and deep flavor.
Heavy Whipping Cream in Desserts
Heavy whipping cream shines in desserts, where its ability to whip into stiff peaks is highly valued. It is commonly used to make whipped cream, mousses, puddings, and frostings. Its lighter texture makes it perfect for creating airy, fluffy desserts that are both delicious and visually appealing. Heavy whipping cream is also a popular choice for topping pies, cakes, and hot beverages like coffee and hot chocolate.
Versatility in Recipes
Both heavy cream and heavy whipping cream are incredibly versatile, making them suitable for a wide range of recipes. Whether you're preparing a savory dish or a sweet treat, these creams can elevate your creations and add a touch of luxury. Their ability to enhance flavor and texture makes them indispensable in any kitchen.
Understanding Fat Content in Cream
The fat content of cream is a crucial factor that determines its texture, flavor, and performance in recipes. Creams with higher fat content are generally thicker, richer, and better suited for whipping, while those with lower fat content are lighter and more fluid. Understanding the fat content of heavy cream and heavy whipping cream will help you make informed decisions when selecting cream for your recipes.
Heavy Cream Fat Content
Heavy cream contains at least 36% milk fat, making it one of the richest types of cream available. This high fat content gives heavy cream its thick, creamy texture and makes it ideal for whipping and creating stable foams. It is also less likely to curdle when used in hot dishes, making it a reliable choice for sauces and soups.
Heavy Whipping Cream Fat Content
Heavy whipping cream has a fat content of 30-36%, which is slightly lower than that of heavy cream. While it is still rich and creamy, its lighter texture makes it better suited for recipes that require a fluffier consistency. Heavy whipping cream is an excellent choice for whipped toppings and desserts, where its ability to whip into stiff peaks is highly valued.
Impact on Recipes
The fat content of cream plays a significant role in the outcome of your recipes. Creams with higher fat content tend to produce richer, more decadent results, while those with lower fat content are lighter and more delicate. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right cream for your recipes and achieve the desired results every time.
Substitutes for Heavy Cream and Heavy Whipping Cream
If you find yourself without heavy cream or heavy whipping cream, there are several substitutes you can use to achieve similar results. While these alternatives may not be identical, they can still provide the richness and texture needed for your recipes.
Half-and-Half
Half-and-half is a blend of equal parts milk and cream, with a fat content of around 10-18%. While it is not as rich as heavy cream or heavy whipping cream, it can be used in recipes that don't require whipping. To increase its fat content and make it more similar to heavy cream, you can add melted butter or a thickening agent like cornstarch.
Coconut Cream
Coconut cream is an excellent dairy-free alternative to heavy cream and heavy whipping cream. It has a rich, creamy texture and a high fat content, making it ideal for whipping and adding richness to recipes. Coconut cream can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, providing a unique flavor that complements a wide range of ingredients.
Other Substitutes
- Evaporated milk mixed with butter.
- Cashew cream for a plant-based option.
- Sour cream or Greek yogurt for a tangy twist.
While these substitutes may not be perfect replacements, they can still help you achieve delicious results in your recipes. Experimenting with different options will allow you to find the best substitute for your specific needs.
Storage Tips for Cream Products
Proper storage is essential to maintaining the quality and freshness of cream products. Whether you're using heavy cream or heavy whipping cream, following these storage tips will help you extend their shelf life and ensure they remain safe to consume.
Refrigeration
Cream products should always be stored in the refrigerator to prevent spoilage. Keep them in their original packaging or transfer them to an airtight container to minimize exposure to air and odors. It's also important to store cream on the top shelf of the refrigerator, where the temperature is most consistent.
Freezing
If you have leftover cream that you won't use before it expires, consider freezing it for later use. While freezing can affect the texture of cream, it is still suitable for cooking and baking. To freeze cream, pour it into an airtight container or freezer-safe bag and label it with the date. Thaw frozen cream in the refrigerator before using it in recipes.
Shelf Life
Unopened cream products typically have a shelf life of several weeks, while opened cream should be used within 7-10 days. Always check the expiration date on the packaging and inspect the cream for signs of spoilage, such as off smells or curdling, before using it in your recipes.
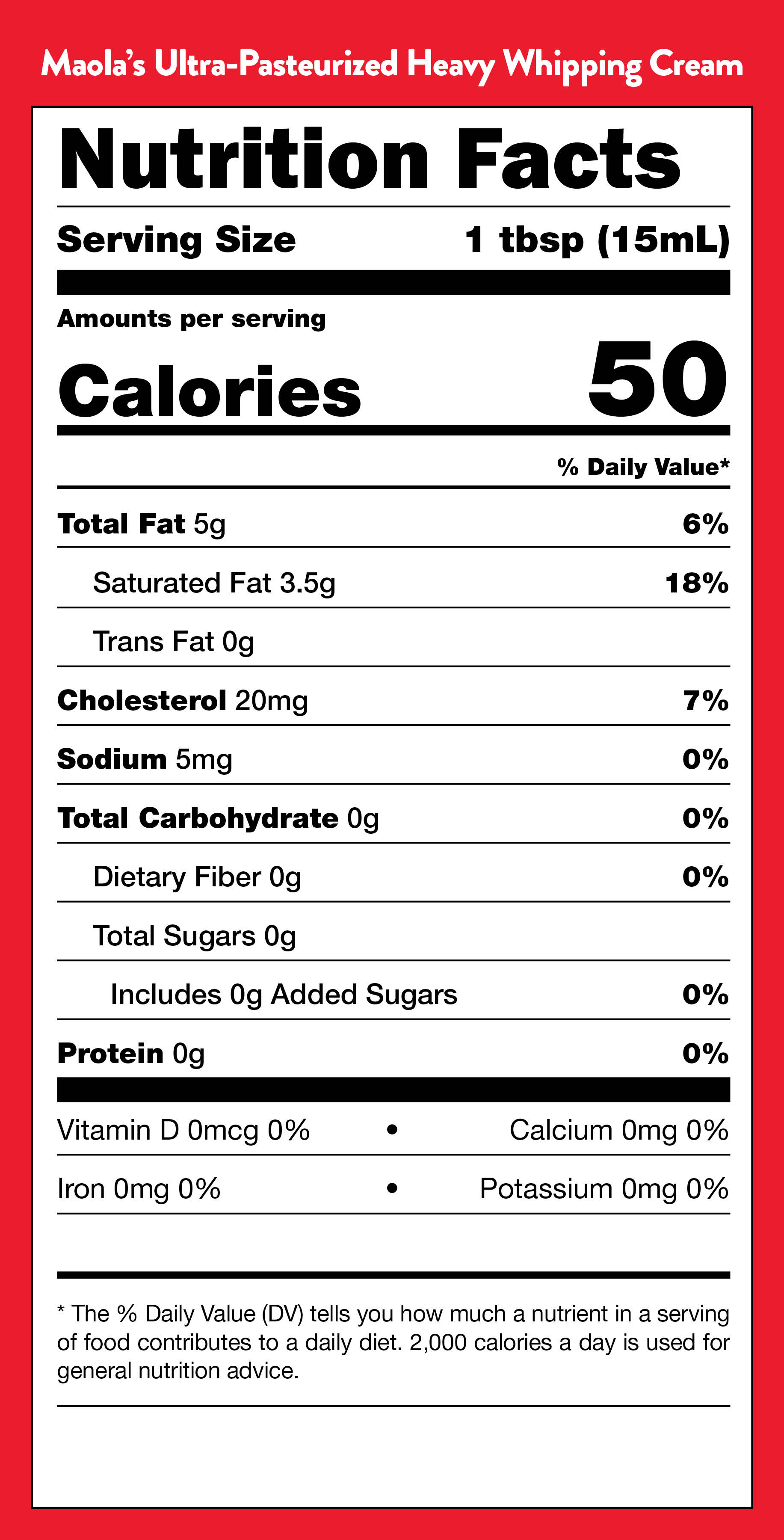
Nutritional Information
Cream products are rich in calories and fat, making them a decadent addition to any dish. However, they also provide essential nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin A, that contribute to overall health. Understanding the nutritional information of heavy cream and heavy whipping