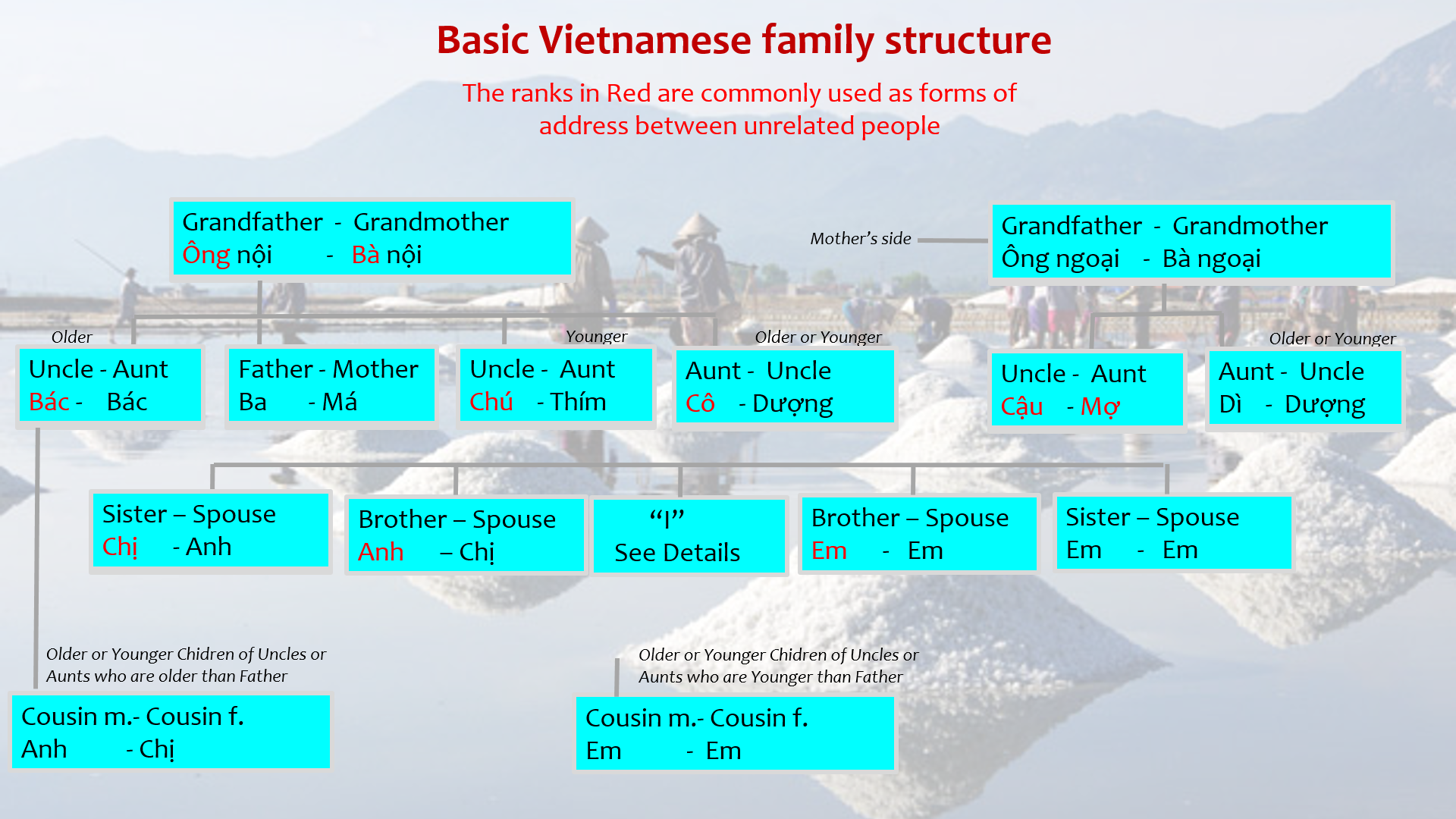
The Vietnamese language is a fascinating linguistic journey that offers a unique window into Vietnam's rich cultural heritage. As one of the most spoken languages in Southeast Asia, Vietnamese presents both challenges and rewards for language enthusiasts. With over 95 million native speakers and millions more learning it worldwide, understanding Vietnamese opens doors to new opportunities in business, travel, and cultural exchange. This comprehensive guide will explore every aspect of the Vietnamese language, from its historical roots to practical learning strategies.
Vietnamese belongs to the Austroasiatic language family, making it distinct from many neighboring languages in Southeast Asia. While sharing geographical proximity with Chinese and Thai speakers, Vietnamese maintains its unique characteristics that have evolved over centuries. The language's tonal nature and complex writing system might seem intimidating at first, but with the right approach, learners can master it effectively. This article will provide valuable insights into the language's structure, pronunciation, and cultural significance.
Whether you're planning to visit Vietnam, considering business opportunities in the region, or simply interested in expanding your linguistic horizons, understanding Vietnamese can be incredibly beneficial. According to recent studies, Vietnam's economy has been growing at an impressive rate, making it an increasingly important player in the global market. This growth has led to a surge in interest in the Vietnamese language, with language learning platforms reporting a 40% increase in Vietnamese course enrollments over the past five years.
Read also:Michelle Stacy A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Career And Achievements
Table of Contents
- The Historical Evolution of Vietnamese
- Understanding the Vietnamese Writing System
- Mastering Vietnamese Pronunciation
- Key Features of Vietnamese Grammar
- The Six Tones of Vietnamese
- Effective Learning Strategies
- Recommended Learning Resources
- Cultural Aspects of Vietnamese Language
- Vietnamese in Business Contexts
- Conclusion and Next Steps
The Historical Evolution of Vietnamese
The Vietnamese language has undergone significant transformations throughout its history. Originally influenced by Chinese during the thousand-year period of Chinese domination (111 BC - 938 AD), Vietnamese absorbed numerous Chinese vocabulary and structural elements. However, despite these influences, Vietnamese maintained its distinct Austroasiatic roots. The language's evolution can be divided into three major periods: ancient Vietnamese, middle Vietnamese, and modern Vietnamese.
During the ancient period, Vietnamese primarily existed as an oral language with various local dialects. The introduction of Chinese characters led to the development of Chu Nom, a modified Chinese character system adapted for Vietnamese. This writing system, used from the 10th to the 20th century, represented a crucial phase in Vietnamese linguistic development. However, its complexity limited widespread literacy among the general population.
Understanding the Vietnamese Writing System
The Vietnamese writing system underwent a revolutionary change in the 20th century with the adoption of Quoc Ngu, the modern Latin-based script. This system, developed by Portuguese missionaries in the 17th century and later refined by French colonial administrators, uses diacritical marks to represent the language's tones and sounds accurately.
The Ancient Chu Nom Script
Chu Nom, meaning "Southern characters," served as Vietnam's traditional writing system for centuries. Key characteristics included:
- Combination of Chinese characters with Vietnamese phonetic elements
- Complex structure requiring extensive memorization
- Limited accessibility for general population
- Used primarily by scholars and government officials
The Modern Quoc Ngu System
Quoc Ngu, adopted as the official writing system in the early 20th century, brought several advantages:
- Based on Latin alphabet with additional diacritics
- Accurate representation of Vietnamese phonetics
- Improved literacy rates nationwide
- Facilitated international communication and learning
Mastering Vietnamese Pronunciation
Vietnamese pronunciation presents unique challenges and opportunities for learners. The language's phonetic system includes 11 distinct vowel sounds and 17 consonant sounds, represented through a combination of letters and diacritical marks. Understanding the proper pronunciation of these sounds is crucial for effective communication.
Read also:Eileen Gu Boyfriend A Closer Look At Her Love Life And Relationships
One of the most distinctive features of Vietnamese pronunciation is its use of initial consonant clusters. Unlike English, Vietnamese allows certain consonant combinations at the beginning of words, such as "tr," "th," and "ph." These clusters require careful attention to articulation. Additionally, Vietnamese vowels often carry different qualities depending on their position in a word, making vowel length and quality important considerations for learners.
Key Features of Vietnamese Grammar
Vietnamese grammar operates on principles that differ significantly from Indo-European languages. The language follows a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) word order, similar to English, but with notable distinctions. One of the most striking features is its lack of grammatical gender and plural forms, making certain aspects of the language relatively straightforward for learners.
Vietnamese utilizes particles and word order to indicate grammatical relationships rather than inflections. For example, tense is expressed through time words rather than verb conjugation. The language also employs measure words extensively, similar to Chinese, requiring speakers to use specific classifiers when referring to nouns. This system adds precision to communication but demands careful attention from learners.
The Six Tones of Vietnamese
Vietnamese is a tonal language with six distinct tones that can change the meaning of words. These tones include:
- Level tone (ngang)
- Rising tone (sắc)
- Falling-rising tone (hỏi)
- Falling tone (nặng)
- High-rising broken tone (ngã)
- Low-falling broken tone (huyền)
Mastering these tones is essential for clear communication. For instance, the syllable "ma" can mean "ghost," "mother," "but," "tomb," "horse," or "rice seedling" depending on its tone. Research conducted by the University of Hawaii's Vietnamese Language Program indicates that approximately 70% of communication errors among learners stem from incorrect tone usage.
Effective Learning Strategies
Developing proficiency in Vietnamese requires a systematic approach that combines multiple learning methods. Successful learners typically follow these strategies:
- Dedicate at least 30 minutes daily to listening practice
- Practice speaking with native speakers through language exchange programs
- Use flashcards for vocabulary acquisition, focusing on common word frequency lists
- Engage in regular writing exercises, starting with simple diary entries
- Watch Vietnamese media with subtitles to improve comprehension
According to a study published in the Journal of Language Teaching and Research, learners who combine these methods show a 40% faster improvement rate compared to those using single-method approaches. The research emphasizes the importance of consistent exposure and active practice in achieving fluency.
Recommended Learning Resources
Modern technology offers numerous resources for Vietnamese language learners. Top recommendations include:
- Memrise and Duolingo apps for structured vocabulary building
- YouTube channels like "Learn Vietnamese with Annie" for authentic pronunciation
- Online dictionaries such as Vdict and TFlat for quick reference
- Textbooks like "Colloquial Vietnamese" for comprehensive grammar study
- Language exchange platforms like iTalki and HelloTalk for speaking practice
These resources provide diverse learning opportunities that cater to different learning styles and preferences. The combination of digital tools and traditional materials creates a robust learning environment that supports long-term language acquisition.
Cultural Aspects of Vietnamese Language
The Vietnamese language is deeply intertwined with the country's cultural values and social norms. One of the most prominent features is the extensive use of honorifics and polite forms of address. Vietnamese speakers typically use different words for "you" and "I" depending on the relative age and social status of the speakers, reflecting the culture's emphasis on respect and hierarchy.
Vietnamese also incorporates numerous proverbs and idiomatic expressions that reveal cultural insights. These expressions often relate to agricultural traditions, family values, and historical experiences. For example, the saying "Ăn quả nhớ kẻ trồng cây" (When eating fruit, remember who planted the tree) emphasizes gratitude and respect for one's benefactors.
Vietnamese in Business Contexts
As Vietnam continues its economic growth, proficiency in Vietnamese has become increasingly valuable in business settings. The country's GDP growth rate has averaged 6-7% annually over the past decade, attracting international investors and business professionals. Understanding Vietnamese can provide significant advantages in negotiations, relationship-building, and market research.
Key sectors where Vietnamese language skills are particularly valuable include:
- Manufacturing and export industries
- Technology and software development
- Tourism and hospitality services
- Education and training programs
- Real estate and property development
According to Vietnam's Ministry of Planning and Investment, foreign businesses with Vietnamese-speaking staff report a 30% higher success rate in market penetration compared to those without language capabilities.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Mastering the Vietnamese language offers numerous benefits, from personal enrichment to professional opportunities. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we've explored the language's historical evolution, writing system, pronunciation challenges, grammatical structure, and cultural significance. The six tones, unique writing system, and rich cultural context make Vietnamese both challenging and rewarding to learn.
To begin your Vietnamese language journey, start by setting clear learning goals and establishing a consistent study routine. Utilize the recommended resources and practice regularly with native speakers. Remember that language learning is a gradual process that requires patience and dedication. Consider joining online communities of Vietnamese language learners to share experiences and progress.
We encourage you to take the next step in your language learning adventure. Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below, and connect with fellow learners who are also exploring the fascinating world of Vietnamese. For more language learning resources, be sure to explore our other articles on Southeast Asian languages and cultural insights.