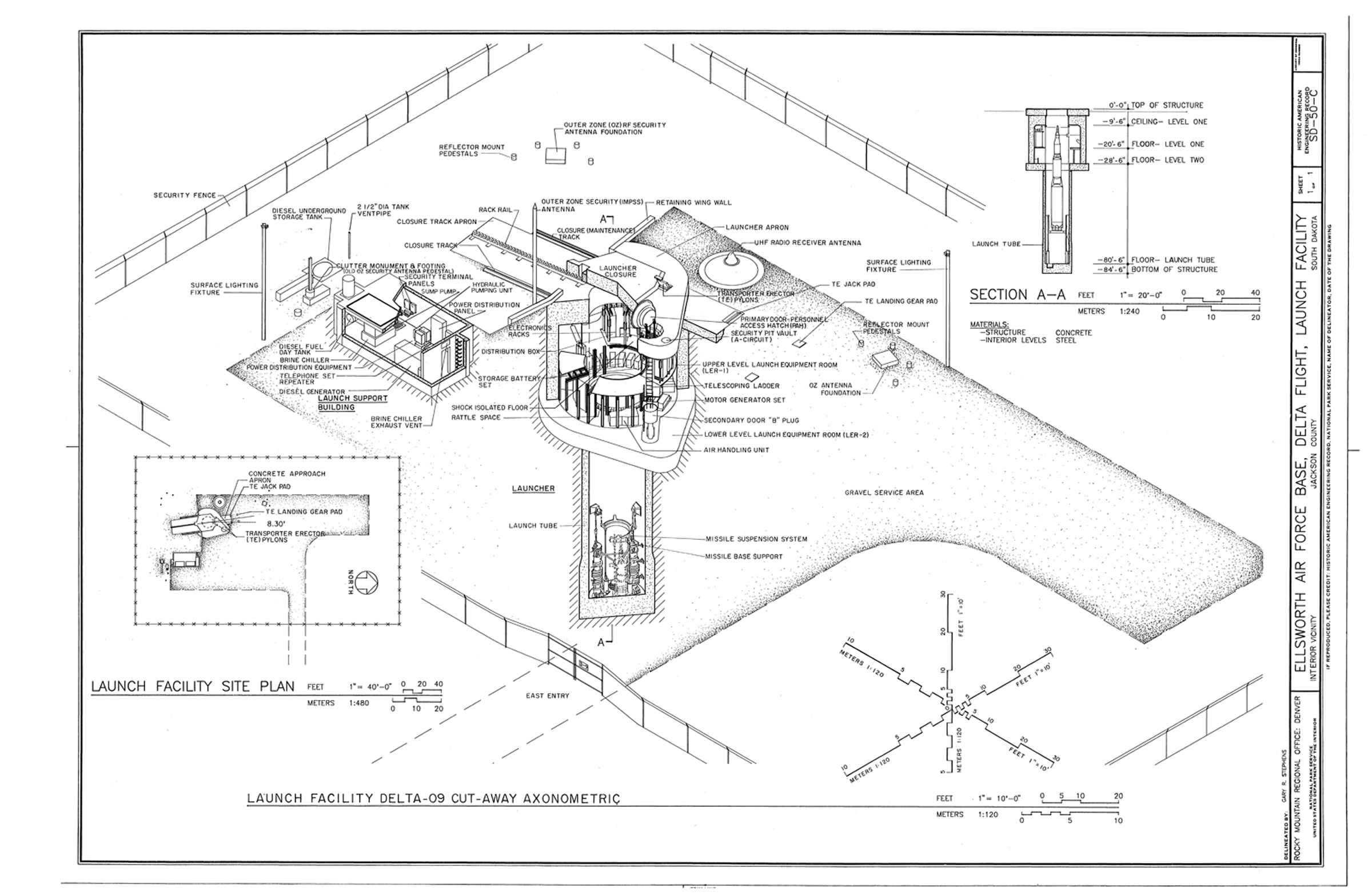
The Minuteman III missile launch is one of the most critical components of the United States' nuclear deterrence strategy. This intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) has been a cornerstone of national security since its introduction in the 1970s. Its ability to deliver nuclear warheads across vast distances makes it a powerful tool for maintaining global peace through deterrence. As we delve into the intricacies of the Minuteman III missile launch, we’ll explore its history, capabilities, and the technology that powers it.
For decades, the Minuteman III has been a symbol of the United States' commitment to safeguarding its citizens and allies. With advancements in technology and geopolitical shifts, understanding the role of this missile system is more important than ever. In this article, we’ll break down the Minuteman III missile launch process, examine its strategic importance, and address the challenges and future prospects of this iconic weapon system.
Whether you're a defense enthusiast, a student of military history, or simply curious about national security, this article will provide you with a detailed and authoritative overview of the Minuteman III missile launch. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how this system works and why it remains relevant in today’s rapidly changing world.
Read also:Nicole Nafziger The Untold Story Of Her Life And Journey
Table of Contents
- History and Development of the Minuteman III Missile
- Technical Specifications of the Minuteman III
- The Minuteman III Missile Launch Process
- Strategic Importance of the Minuteman III
- Modernization Efforts and Upgrades
- Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Minuteman III
- Future Prospects of the Minuteman III System
- Comparison with Other ICBM Systems
- Impact on Global Security and Stability
- Conclusion and Call to Action
History and Development of the Minuteman III Missile
The Minuteman III missile is the third generation of the Minuteman series, which was first introduced in the 1960s. Developed by Boeing, the Minuteman III entered service in 1970 and was designed to replace its predecessors, the Minuteman I and II. The primary goal of this missile system was to enhance the United States' nuclear deterrence capabilities during the Cold War.
One of the key innovations of the Minuteman III was its ability to carry multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs). This advancement allowed a single missile to deliver multiple warheads to different targets, significantly increasing its strategic value. The development of the Minuteman III was driven by the need to counter the growing nuclear capabilities of the Soviet Union.
Over the years, the Minuteman III has undergone numerous upgrades to ensure its reliability and effectiveness. These upgrades have included improvements to its guidance systems, propulsion, and warhead technology. Despite being over 50 years old, the Minuteman III remains a vital part of the U.S. nuclear arsenal.
Technical Specifications of the Minuteman III
The Minuteman III missile is a highly sophisticated weapon system with impressive technical specifications. Below is a table summarizing its key features:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Length | 61 feet (18.5 meters) |
| Diameter | 5.5 feet (1.7 meters) |
| Weight | 79,432 pounds (36,030 kg) |
| Range | 6,000+ miles (9,656+ km) |
| Warhead | Up to 3 MIRVs |
| Propulsion | Three-stage solid-fuel rocket |
The Minuteman III’s three-stage solid-fuel rocket design allows for rapid deployment and high reliability. Its ability to carry multiple warheads makes it a formidable deterrent against potential adversaries. The missile’s guidance system is highly accurate, ensuring precise targeting even over long distances.
Components of the Minuteman III Missile
- First Stage: Provides initial thrust to lift the missile off the ground.
- Second Stage: Continues the missile's ascent into the atmosphere.
- Third Stage: Propels the missile into space and toward its target.
- Reentry Vehicles: Houses the warheads and ensures their safe delivery to the target.
Each component of the Minuteman III is meticulously designed to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The missile’s solid-fuel propulsion system is particularly noteworthy, as it allows for quick launch times and minimal maintenance requirements.
Read also:Joel Bushby Brothers The Untold Story Of Adventure And Bonding
The Minuteman III Missile Launch Process
The Minuteman III missile launch process is a highly coordinated operation that involves multiple stages and strict protocols. This process ensures that the missile is launched safely and accurately, minimizing the risk of errors or accidents.
The launch process begins with a command from the National Command Authority (NCA), which is typically the President of the United States. Once the order is given, it is transmitted to the missile launch control centers (LCCs), where two-person teams verify the authenticity of the command.
Steps in the Minuteman III Missile Launch Process
- Command Authorization: The launch order is verified and authenticated by the missile launch crew.
- Key Activation: Both members of the launch crew must simultaneously turn their keys to initiate the launch sequence.
- Missile Ignition: The missile’s solid-fuel rocket engines ignite, propelling it out of the silo.
- Flight Trajectory: The missile follows a pre-programmed trajectory toward its target.
- Warhead Deployment: The reentry vehicles separate and deliver the warheads to their designated targets.
This process is designed to be fail-safe, with multiple layers of security and redundancy to prevent unauthorized launches. The Minuteman III’s launch system is a testament to the precision and reliability of modern missile technology.
Strategic Importance of the Minuteman III
The Minuteman III missile plays a crucial role in the United States' nuclear deterrence strategy. Its ability to deliver multiple warheads over long distances makes it a powerful tool for maintaining global stability and preventing nuclear conflict.
One of the key aspects of the Minuteman III’s strategic importance is its role in the nuclear triad. The nuclear triad consists of three components: land-based ICBMs, submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers. The Minuteman III is the land-based component of this triad, providing a rapid and reliable means of retaliation in the event of a nuclear attack.
In addition to its deterrence capabilities, the Minuteman III serves as a symbol of U.S. military strength and technological superiority. Its presence in the nuclear arsenal sends a clear message to potential adversaries that any attack on the United States or its allies will be met with overwhelming force.
Role in Global Stability
- Deterrence: Prevents adversaries from launching a nuclear attack by ensuring a credible threat of retaliation.
- Reassurance: Provides assurance to allies that the United States is committed to their defense.
- Technological Superiority: Demonstrates the United States' leadership in missile technology and innovation.
By maintaining a robust and reliable Minuteman III missile system, the United States reinforces its position as a global leader in nuclear deterrence and security.
Modernization Efforts and Upgrades
Despite its age, the Minuteman III remains a critical component of the U.S. nuclear arsenal. However, to ensure its continued effectiveness, the U.S. government has invested heavily in modernization efforts and upgrades. These efforts aim to extend the missile’s service life and enhance its capabilities.
One of the key areas of focus for modernization is the missile’s guidance system. Advances in technology have enabled the development of more accurate and reliable guidance systems, improving the missile’s targeting precision. Additionally, upgrades to the missile’s propulsion system have increased its range and payload capacity.
Upcoming Upgrades and Replacements
- Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD): A planned replacement for the Minuteman III, expected to enter service in the 2030s.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: Improvements to protect the missile system from cyber threats.
- Warhead Modernization: Development of new warhead designs to replace aging components.
These modernization efforts underscore the United States' commitment to maintaining a credible and effective nuclear deterrent. By investing in the Minuteman III and its eventual replacement, the U.S. ensures its ability to respond to evolving threats and challenges.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Minuteman III
While the Minuteman III missile is a vital component of U.S. national security, it is not without its challenges and controversies. Critics have raised concerns about the missile’s age, cost, and potential risks associated with its continued operation.
One of the primary challenges facing the Minuteman III is its aging infrastructure. Many of the missile’s components were designed and manufactured over 50 years ago, raising questions about their reliability and maintainability. Additionally, the cost of maintaining and upgrading the system has become a point of contention, with some arguing that resources could be better spent on other defense priorities.
Another area of controversy is the ethical and strategic implications of maintaining a large nuclear arsenal. Critics argue that the continued reliance on nuclear weapons undermines efforts to promote global disarmament and reduce the risk of nuclear conflict.
Addressing the Challenges
- Investment in Modernization: Ensuring the missile system remains reliable and effective.
- Transparency and Accountability: Addressing public concerns about the cost and risks of the system.
- Diplomatic Efforts: Engaging in arms control negotiations to reduce the global nuclear threat.
By addressing these challenges head-on, the United States can continue to rely on the Minuteman III as a cornerstone of its national security strategy while working toward a safer and more stable world.
Future Prospects of the Minuteman III System
The future of the Minuteman III missile system is closely tied to ongoing modernization efforts and the development of its replacement, the Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD). As the Minuteman III approaches the end of its service life, the U.S. government is preparing for a transition to a new generation of ICBMs.
The GBSD program represents a significant investment in the future of U.S. nuclear deterrence. Designed to replace the Minuteman III, the GBSD will incorporate the latest advancements in missile technology, including improved guidance systems, propulsion, and warhead capabilities. The program is expected to enter service in the 2030s, ensuring the continuity of the U.S. nuclear triad.
Key Objectives of the GBSD Program
- Enhanced Reliability: Ensuring the new system is more reliable and maintainable than its predecessor.
- Improved Accuracy: Incorporating advanced guidance systems for greater targeting precision.
- Extended Service Life: Designing the system to remain operational for several decades.
As the Minuteman III transitions to the GBSD, the United States will continue to uphold its commitment to nuclear deterrence and